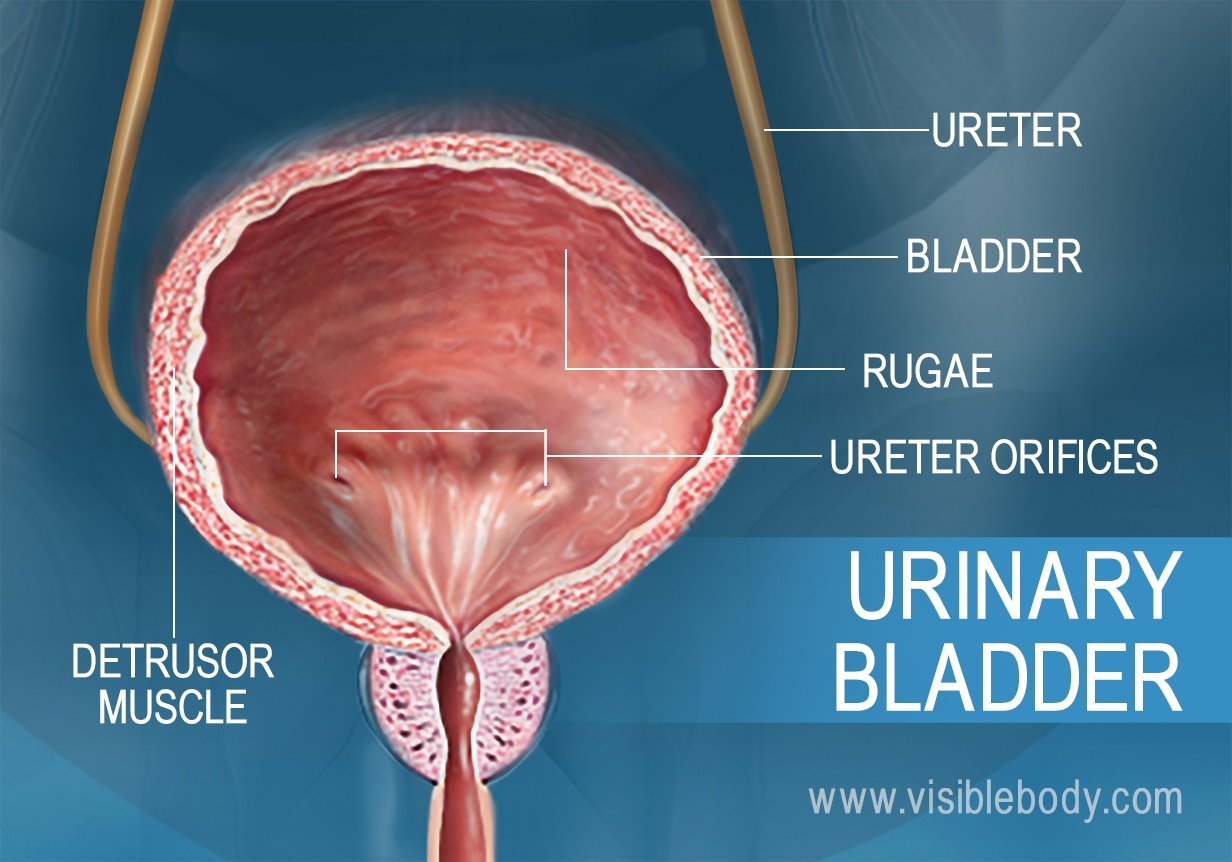
Bladder Water Reabsorption . urine is formed in three steps: Filtration involves the transfer of soluble components, such as water and waste, from the blood into the glomerulus. Summarize the steps in urine formation. this is the first report which exhibits water absorption from urine within the human urinary bladder in the fully physiological. Glomerular filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. there are three main steps of urine formation: compare and contrast passive and active tubular reabsorption; Explain why the differential permeability or impermeability. These processes ensure that only waste and. reabsorption is a finely tuned process that is altered to maintain homeostasis of blood volume, blood pressure, plasma osmolarity, and blood ph. Explain the role of the loop of henle, the vasa recta, and the. describe how and where water, organic compounds, and ions are reabsorbed in the nephron.
from www.visiblebody.com
Glomerular filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. there are three main steps of urine formation: Filtration involves the transfer of soluble components, such as water and waste, from the blood into the glomerulus. compare and contrast passive and active tubular reabsorption; reabsorption is a finely tuned process that is altered to maintain homeostasis of blood volume, blood pressure, plasma osmolarity, and blood ph. Explain the role of the loop of henle, the vasa recta, and the. this is the first report which exhibits water absorption from urine within the human urinary bladder in the fully physiological. urine is formed in three steps: Summarize the steps in urine formation. Explain why the differential permeability or impermeability.
Urinary System Structures
Bladder Water Reabsorption describe how and where water, organic compounds, and ions are reabsorbed in the nephron. Summarize the steps in urine formation. These processes ensure that only waste and. there are three main steps of urine formation: Explain the role of the loop of henle, the vasa recta, and the. Glomerular filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. describe how and where water, organic compounds, and ions are reabsorbed in the nephron. urine is formed in three steps: this is the first report which exhibits water absorption from urine within the human urinary bladder in the fully physiological. reabsorption is a finely tuned process that is altered to maintain homeostasis of blood volume, blood pressure, plasma osmolarity, and blood ph. compare and contrast passive and active tubular reabsorption; Explain why the differential permeability or impermeability. Filtration involves the transfer of soluble components, such as water and waste, from the blood into the glomerulus.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Urinary System PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6880197 Bladder Water Reabsorption Explain the role of the loop of henle, the vasa recta, and the. reabsorption is a finely tuned process that is altered to maintain homeostasis of blood volume, blood pressure, plasma osmolarity, and blood ph. urine is formed in three steps: compare and contrast passive and active tubular reabsorption; Explain why the differential permeability or impermeability. Filtration. Bladder Water Reabsorption.
From www.youtube.com
water reabsorption in frog urinary bladder YouTube Bladder Water Reabsorption Glomerular filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. describe how and where water, organic compounds, and ions are reabsorbed in the nephron. urine is formed in three steps: reabsorption is a finely tuned process that is altered to maintain homeostasis of blood volume, blood pressure, plasma osmolarity, and blood ph. this is the first report which exhibits water absorption. Bladder Water Reabsorption.
From schematicfixashiver.z21.web.core.windows.net
Nephron Reabsorption And Secretion Diagram Bladder Water Reabsorption there are three main steps of urine formation: this is the first report which exhibits water absorption from urine within the human urinary bladder in the fully physiological. Explain why the differential permeability or impermeability. describe how and where water, organic compounds, and ions are reabsorbed in the nephron. compare and contrast passive and active tubular. Bladder Water Reabsorption.
From www.linstitute.net
CIE A Level Biology复习笔记14.1.5 Formation of Urine翰林国际教育 Bladder Water Reabsorption Filtration involves the transfer of soluble components, such as water and waste, from the blood into the glomerulus. this is the first report which exhibits water absorption from urine within the human urinary bladder in the fully physiological. describe how and where water, organic compounds, and ions are reabsorbed in the nephron. urine is formed in three. Bladder Water Reabsorption.
From www.pinterest.com
The Urinary System Physiology, Biology notes, Med student Bladder Water Reabsorption urine is formed in three steps: Explain why the differential permeability or impermeability. Filtration involves the transfer of soluble components, such as water and waste, from the blood into the glomerulus. Explain the role of the loop of henle, the vasa recta, and the. describe how and where water, organic compounds, and ions are reabsorbed in the nephron.. Bladder Water Reabsorption.
From www.researchgate.net
Proximal tubular Na ⁺ reabsorption. Active Na⁺ transport mediated by Bladder Water Reabsorption reabsorption is a finely tuned process that is altered to maintain homeostasis of blood volume, blood pressure, plasma osmolarity, and blood ph. Summarize the steps in urine formation. urine is formed in three steps: These processes ensure that only waste and. describe how and where water, organic compounds, and ions are reabsorbed in the nephron. Explain the. Bladder Water Reabsorption.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
Tubular Reabsorption Anatomy and Physiology I Bladder Water Reabsorption Filtration involves the transfer of soluble components, such as water and waste, from the blood into the glomerulus. These processes ensure that only waste and. compare and contrast passive and active tubular reabsorption; Explain why the differential permeability or impermeability. Explain the role of the loop of henle, the vasa recta, and the. this is the first report. Bladder Water Reabsorption.
From slideplayer.com
Part 3 Kidney and Excretion ppt download Bladder Water Reabsorption Summarize the steps in urine formation. Filtration involves the transfer of soluble components, such as water and waste, from the blood into the glomerulus. Explain the role of the loop of henle, the vasa recta, and the. These processes ensure that only waste and. Glomerular filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. reabsorption is a finely tuned process that is altered to. Bladder Water Reabsorption.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Figure 25.13 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6153805 Bladder Water Reabsorption there are three main steps of urine formation: Summarize the steps in urine formation. Glomerular filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. this is the first report which exhibits water absorption from urine within the human urinary bladder in the fully physiological. compare and contrast passive and active tubular reabsorption; reabsorption is a finely tuned process that is altered. Bladder Water Reabsorption.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT F214 Communication, Homeostasis and Energy 4.2.1 Ultrafiltration Bladder Water Reabsorption there are three main steps of urine formation: Filtration involves the transfer of soluble components, such as water and waste, from the blood into the glomerulus. Summarize the steps in urine formation. Explain why the differential permeability or impermeability. Explain the role of the loop of henle, the vasa recta, and the. Glomerular filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. compare. Bladder Water Reabsorption.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
The Urinary System and Homeostasis Water and Electrolyte balance Bladder Water Reabsorption Explain the role of the loop of henle, the vasa recta, and the. Glomerular filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. compare and contrast passive and active tubular reabsorption; Explain why the differential permeability or impermeability. this is the first report which exhibits water absorption from urine within the human urinary bladder in the fully physiological. These processes ensure that only. Bladder Water Reabsorption.
From open.oregonstate.education
25.5 Physiology of Urine Formation Tubular Reabsorption and Secretion Bladder Water Reabsorption Summarize the steps in urine formation. urine is formed in three steps: describe how and where water, organic compounds, and ions are reabsorbed in the nephron. compare and contrast passive and active tubular reabsorption; Explain why the differential permeability or impermeability. reabsorption is a finely tuned process that is altered to maintain homeostasis of blood volume,. Bladder Water Reabsorption.
From www.bio1152.nicerweb.com
nephron_urine.html 44_14Nephron_L.jpg Bladder Water Reabsorption urine is formed in three steps: Summarize the steps in urine formation. reabsorption is a finely tuned process that is altered to maintain homeostasis of blood volume, blood pressure, plasma osmolarity, and blood ph. there are three main steps of urine formation: Filtration involves the transfer of soluble components, such as water and waste, from the blood. Bladder Water Reabsorption.
From med.libretexts.org
24.3D Tubular Reabsorption Medicine LibreTexts Bladder Water Reabsorption These processes ensure that only waste and. Glomerular filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. there are three main steps of urine formation: describe how and where water, organic compounds, and ions are reabsorbed in the nephron. Explain why the differential permeability or impermeability. reabsorption is a finely tuned process that is altered to maintain homeostasis of blood volume, blood. Bladder Water Reabsorption.
From open.oregonstate.education
25.5 Physiology of Urine Formation Tubular Reabsorption and Secretion Bladder Water Reabsorption Glomerular filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. reabsorption is a finely tuned process that is altered to maintain homeostasis of blood volume, blood pressure, plasma osmolarity, and blood ph. Filtration involves the transfer of soluble components, such as water and waste, from the blood into the glomerulus. These processes ensure that only waste and. Explain why the differential permeability or impermeability.. Bladder Water Reabsorption.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
The Urinary System and Homeostasis Water and Electrolyte balance Bladder Water Reabsorption Summarize the steps in urine formation. compare and contrast passive and active tubular reabsorption; Filtration involves the transfer of soluble components, such as water and waste, from the blood into the glomerulus. there are three main steps of urine formation: These processes ensure that only waste and. Explain why the differential permeability or impermeability. Explain the role of. Bladder Water Reabsorption.
From schoolbag.info
Figure 10.5. Reabsorption and Secretion in the Nephron Bladder Water Reabsorption Explain why the differential permeability or impermeability. reabsorption is a finely tuned process that is altered to maintain homeostasis of blood volume, blood pressure, plasma osmolarity, and blood ph. there are three main steps of urine formation: Summarize the steps in urine formation. Explain the role of the loop of henle, the vasa recta, and the. These processes. Bladder Water Reabsorption.
From www.visiblebody.com
Urine Creation Bladder Water Reabsorption Glomerular filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Summarize the steps in urine formation. reabsorption is a finely tuned process that is altered to maintain homeostasis of blood volume, blood pressure, plasma osmolarity, and blood ph. urine is formed in three steps: this is the first report which exhibits water absorption from urine within the human urinary bladder in the. Bladder Water Reabsorption.